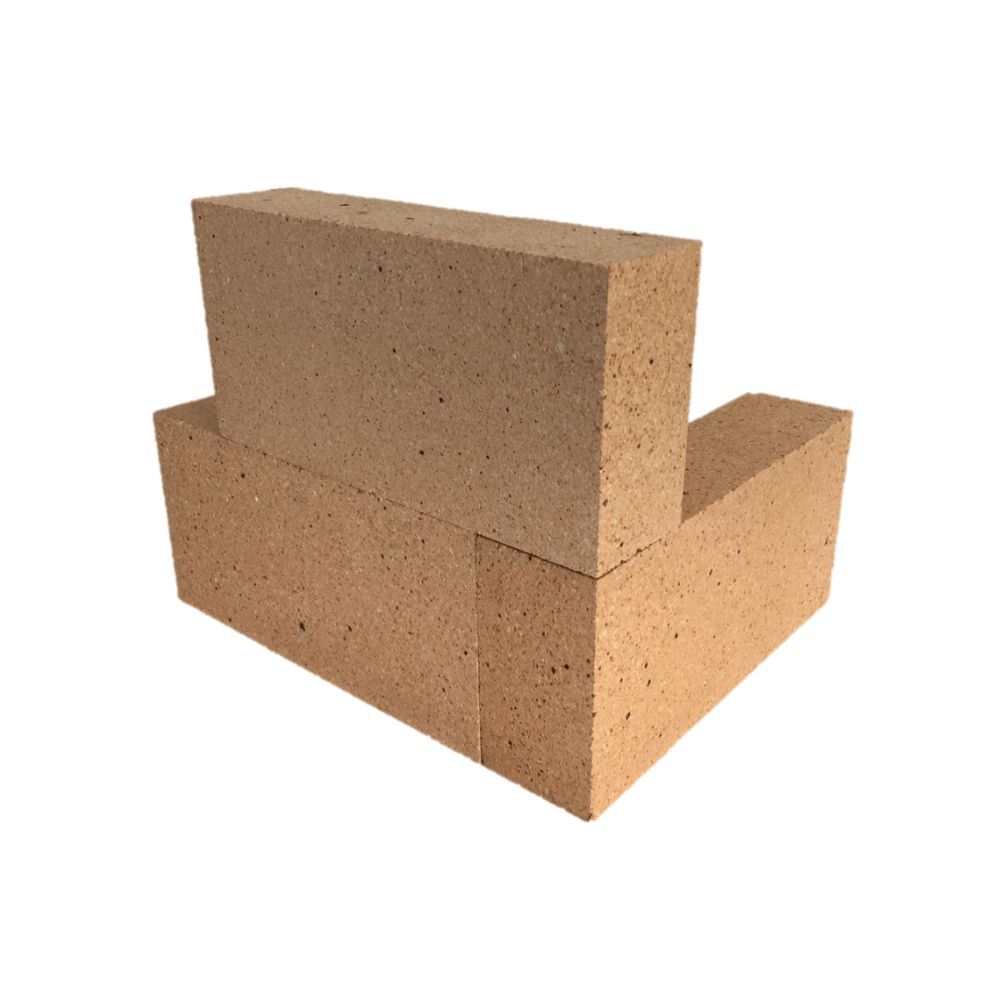

Refractoriness is the ability of a material to withstand high temperatures without melting, softening, or deforming. Refractory bricks are specially engineered to maintain structural integrity under extreme heat.
The term NF2 is a designation used in some industries or standards to classify refractory bricks according to their chemical composition, thermal properties, and resistance to thermal shock. While the exact specifications of NF2 might vary based on the standard or manufacturer, it generally signifies:
- Neutral Composition:
- NF2 bricks often belong to the neutral refractories category, which means they are chemically stable and do not react with acidic or basic slags.
- Materials such as alumina (Al₂O₃) and chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) are commonly used in neutral bricks.
- High Alumina Content:
- NF2 bricks typically have a high alumina content (Al₂O₃), ranging between 45-70%, contributing to excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength.
- Thermal Shock Resistance:
- NF2 refractory bricks exhibit good resistance to thermal cycling, meaning they can endure rapid temperature changes without cracking.
- Specific Applications:
- NF2 bricks are widely used in steel furnaces, cement kilns, and glass manufacturing where both high heat and chemically reactive environments are present.
- Refractoriness Under Load (RUL):
- The bricks maintain their structural integrity under mechanical stress at elevated temperatures, making them suitable for applications like furnace linings.
- Standardization:
- NF2 may correspond to a specific grade under standards like DIN, ASTM, or ISO. If you’re dealing with a supplier or industry standard, cross-referencing their specification sheet will clarify exact parameters like maximum temperature limits and chemical composition.
Key Properties of NF2 Refractory Bricks
- Operating Temperature: Typically withstand temperatures of up to 1400-1600°C, depending on the exact composition.
- Chemical Stability: Resistant to acidic and basic environments, making them versatile in various industrial settings.
- Durability: High wear resistance and ability to handle mechanical stress over long operating periods.
Refractory bricks come in a wide range of sizes and shapes, depending on their application and the furnace or equipment they are used in. The sizes can generally be categorized into standard sizes, customized shapes, and specialty bricks. Here’s an overview:
1. Standard Sizes
Most refractory bricks are manufactured in standard dimensions for common applications. These sizes vary slightly based on regional and industrial standards. Commonly used standard sizes include:
- 230 mm x 114 mm x 65 mm (9 in x 4.5 in x 2.5 in): Known as the “firebrick standard size,” this is widely used in furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces.
- 230 mm x 114 mm x 75 mm (9 in x 4.5 in x 3 in): Slightly thicker than the standard size for heavy-duty applications.
- 300 mm x 150 mm x 75 mm (12 in x 6 in x 3 in): Used for larger industrial installations.
These sizes are ideal for straight lining and flat surfaces.
2. Splits (Thin Bricks)
For applications requiring thinner bricks, splits are used. Common sizes for splits include:
- 230 mm x 114 mm x 32 mm (9 in x 4.5 in x 1.25 in): Thin bricks for specialized linings or repairs.
3. Tile Shapes
Some applications, like kilns and furnaces, require refractory tiles. Typical sizes include:
- 230 mm x 230 mm x 50 mm (9 in x 9 in x 2 in): Square tiles for flat linings.
4. Special Shapes
Refractory bricks are often manufactured in custom shapes to fit specific industrial needs. These include:
- Arch Bricks: Used for building circular linings, such as in chimneys or rotary kilns. Sizes vary depending on the radius of the structure.
- Wedge Bricks: For constructing arches or domes.
- Key Bricks: Designed to lock into place for structural stability in arches.
- End Bricks or Corner Bricks: Made for corners or edges in rectangular or circular structures.
5. Customized and Specialty Bricks
For unique furnace designs, customized bricks are made to order. These can be tailored in:
- Size
- Shape (curved, triangular, trapezoidal, etc.)
- Thickness (thin to thick depending on thermal insulation needs)
6. Modular Bricks for Insulating Layers
In modern refractory installations, modular bricks with precise interlocking mechanisms are gaining popularity for quick assembly and better thermal insulation.
Industry-Specific Sizes
The exact size of refractory bricks depends on their application:
- Steel Furnaces: Larger and thicker bricks for durability under extreme conditions.
- Cement Kilns: Special shapes like taper bricks or cylindrical bricks for rotary structures.
- Fireplaces and Stoves: Standard 230 mm x 114 mm x 65 mm bricks for residential use.
Custom Size Factors
Custom refractory brick sizes are influenced by:
- The shape of the furnace or kiln.
- The operating temperature and load conditions.
- The need to minimize the number of joints, which are weak points in the lining.



Recent Comments