Understanding the CPU: The Heart of Your Computer
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, is a crucial electronic component responsible for executing instructions and processing data. It performs the fundamental operations of a computer system, including arithmetic calculations, logic operations, and control functions.
Key Functions of the CPU
- Instruction Execution: The CPU interprets and executes instructions from programs stored in memory. This involves fetching the instruction, decoding it, and then executing it.
- Arithmetic and Logic Operations: The CPU performs basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT).
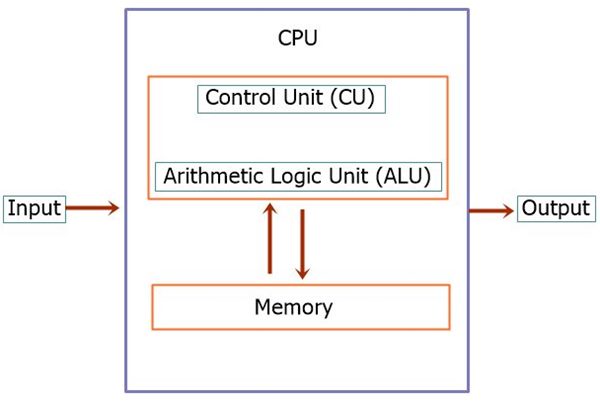
- Control Unit: The CPU contains a control unit that directs the operation of the processor. It manages the flow of data between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices.
- Registers: These are small storage locations within the CPU that temporarily hold data and instructions being processed. Registers enable faster data access compared to accessing main memory.
Components of the CPU
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit): Responsible for performing arithmetic and logic operations.
- Control Unit: Coordinates the activities of the CPU and manages the data flow between the CPU and other components.
- Cache Memory: A small amount of high-speed memory located within the CPU, used to store frequently accessed data and instructions, enhancing performance.
Types of CPUs
- Single-Core CPUs: Contain one core, capable of executing one instruction at a time. Suitable for basic tasks.
- Multi-Core CPUs: Feature multiple cores (dual-core, quad-core, etc.), allowing for parallel processing and improved performance for multitasking and demanding applications.
Performance Factors
- Clock Speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), it indicates how many cycles per second the CPU can execute. Higher clock speeds generally lead to better performance.
- Architecture: The design of the CPU (e.g., x86, ARM) affects its efficiency and compatibility with software.
- Cache Size: Larger cache sizes can significantly enhance performance by reducing the time it takes to access data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CPU is a vital electronic component that plays a significant role in the functionality of computers and devices. Understanding its components and functions can help users appreciate the power and capabilities of their systems.



Recent Comments